Transport operators in Brazilian cities are facing their worst crisis ever. Inefficient transport networks lead to overcrowded buses and trains and hours of traffic congestion every day. The way transport is being planned demands a new way of thinking. Innovative digital solutions like on-demand transport provide access to products and services that are flexible and user-centric and can radically rethink the way people move.
What is on-demand ridepooling?
This is a transport service in which each passenger can individually determine his or her starting point and destination and a vehicle is then assigned by the system. At the same time, passengers requesting similar routes are combined in the same vehicle to optimize the journey. The algorithm distributes passengers among vehicles in such a way that detours in each journey are kept to a minimum. For this kind of service, at least three platforms are required: a passenger app, a driver app and a management platform. Behind all of this is the algorithm that optimizes the route. What’s important is that software like that from door2door can be integrated into the public transport operator’s system. In this way, operators can work with their own drivers and fleet with the goal of attracting passengers, optimizing routes and reducing operating costs.
What are the benefits of on-demand transport?
On-demand transport increases ridership by improving the service coverage. The operating area and number of stops are fully flexible and defined with the service provider, in line with local needs. By increasing the service coverage, the distance passengers need to walk can be reduced, increasing their safety and mobility without the need for a bus stop infrastructure.
Because the service is set up digitally, diverse use cases can be easily applied. New residential areas can be connected to the city center or local stations, shuttle services can take employees to their workplace, and services can run to fixed venues such as airports or events, such as football games or concerts. The technology allows the same fleet to be used for different services, so that better use can be made of the existing infrastructure. More details about the potential of the combination of use cases and its benefits can be found in our white paper.
On-demand transport can also benefit the local economy. Within the operating area, it is possible to include local restaurants or shops in the grid of virtual stops, allowing users to book rides from and to these locations. This enables the on-demand ridepooling system to be deeply integrated into the local economy, which helps increase acceptance of and identification with the system.
Moreover, the technology offers a benefit to all users, including people with physical disabilities, visual impairments or those without smartphones. All digital solutions are adapted to provide accessibility features which, when combined with an accessible fleet, can offer an inclusive service for all. For instance, the passenger app allows wheelchair users to book a ride, and the driver will be informed in advance that assistance may be needed. The algorithm automatically assigns a vehicle that is wheelchair accessible.
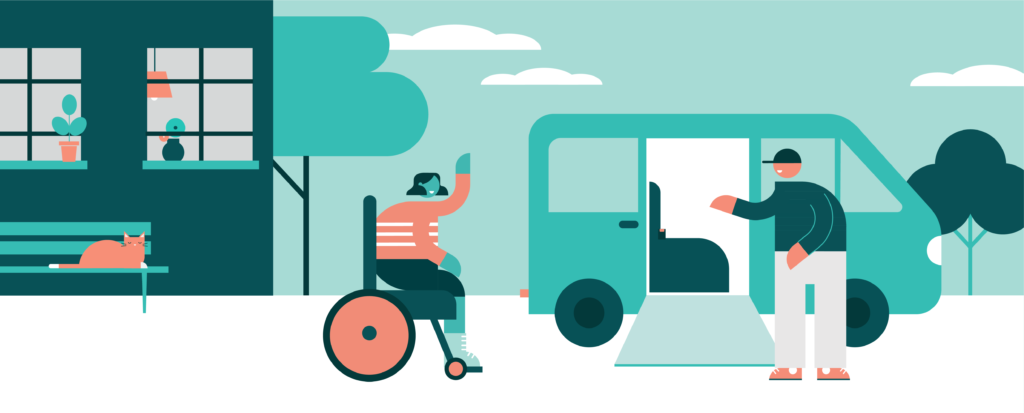

The success of the services can be monitored and corrected almost hourly with the help of transparent data. With a demand-based, digital approach, ridepooling breaks down inefficient structures and optimizes existing offers.
The combination of these characteristics has made ridepooling one of the dominating innovation topics in the public transportation industry in recent years. A growing number of technology providers have been racing to develop the best product market fit in order to secure a favourable market share with this emerging trend. Currently there are over 270 active ridepooling projects in the world, most of them launched in the last three years in Europe and the United States. On-demand ridepooling services first started in Brazil in 2019 and the solution has already raised interest in many cities.
Why is it time to rethink public transport in Brazil?
In most cities in Brazil, public transport operators receive no subsidy from local governments and rely on ticket fares to cover operating costs. Therefore, operators are fully dependent on ridership. This funding model poses the challenge of developing affordable and efficient transport for passengers.
As a consequence of this funding model, local public transport operators are facing one of their biggest financial crises ever. In the past years, they have been losing passengers due to inefficiency and the high cost for passengers. The situation was intensified when B2C ride-hailing services entered the market with similar prices, providing an individual, fast and comfortable alternative. COVID-19 directly affected the operators’ revenue, as ridership fell by 40.8% in 2020. As a consequence, operators reduced 20.8% of the service offering and laid off more than 66 thousand employees in the country.¹
It is time to start looking at alternative ways of financing public transport operations and rethink how mobility is offered to the population. Worldwide, public transport is subsidized to reduce the costs that passengers incur. As with other social rights in the urban environment, public transport should be financed by alternative means. In this way, the higher cost coverage would not only promote inclusion, but also open space for operators to bring innovative projects to the streets.
Mobility is set to change considerably over the next few years, and this change will certainly include digital innovations in transportation. The technologies are already there, ready to make transportation more efficient, safe and sustainable. The market demands innovative transit solutions and a radical rethinking of transportation. It’s time to build a reliable, affordable and accessible public transport – on-demand ridepooling is a strong instrument that is capable of contributing to the transition of Brazilian urban mobility. Have a look here at how door2door has been innovating mobility in Europe and can bring the future of public transport to Brazil. And lastly, if you want to stay updated on the development of the Brazilian market, follow us on our LinkedIn page.
Footnote
1. Boletim NTU <https://ntu.org.br/novo/upload/Publicacao/Pub637523537674807205.pdf>